Integrating OpenEvidence LLM into UCSF Epic for Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Support
1. The UCSF Health problem
1. The UCSF Health problem
The UCSF Health problem: Cancer survivors at UCSF Health have unmet needs significantly impacting their health-related quality of life (HRQOL). These include managing ongoing side effects of treatment, surveillance for cancer recurrence, informational needs, health promotion and coordination of care. A Survivorship Care Plan (SCPs) is a document that is completed at the completion of curative cancer treatment when the patient is transitioning to survivorship care.
1. The UCSF Health Problem
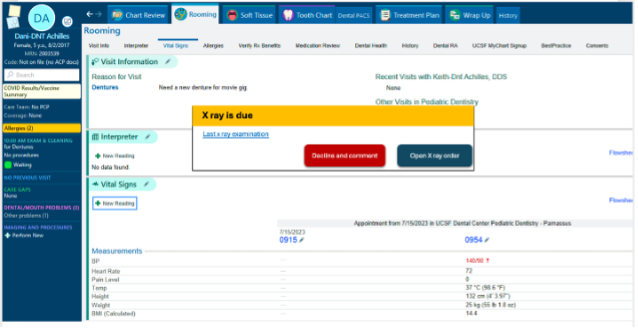
Orthodontic treatment requires regular radiographic imaging to monitor tooth movement, ensure proper bracket positioning and evaluate the risk of root resorption [1]. However, due to long term orthodontic treatment (average of 24 months), it is not uncommon for orthodontists to occasionally overlook the timing of radiographs, potentially leading to delayed treatment adjustments and prolonged overall treatment duration. Additionally, orthodontic patients should receive dental checkups and cleanings every six months, or more frequently, if necessary, to maintain oral health and prevent issues such as interproximal caries. Unfortunately, orthodontists may overlook these routine reminders, increasing the risk of caries development during treatment [2,3].
A solution is needed to automatically track patient radiographic and dental cleaning records, issuing timely reminders to ensure adherence to these critical steps in the orthodontic workflow. Previous attempts at addressing similar issues include manual tracking and reminders from administrative staff, but these approaches are prone to human error. The intended end-users of this solution include orthodontists, dental assistants, and administrative staff who manage patient records and appointments.
2. How Might AI Help?
AI can assist in monitoring and analyzing patient records by identifying patterns and issuing timely reminders. The AI system would utilize patient electronic health records, including past radiographs and dental cleaning history, to track due dates for necessary imaging and oral hygiene appointments.
The AI model would produce automated reminders when a patient is due for a radiograph or dental cleaning, ensuring timely intervention. It would help solve the problem by reducing the likelihood of missed imaging or hygiene appointments, thereby improving treatment efficiency and preventing oral health complications.
3. How Would an End-User Find and Use It?
The AI support would be integrated into the existing orthodontic patient management system (Apex), functioning within the standard workflow. When a patient’s record is accessed, the system would check whether an X-ray or cleaning is due based on predefined intervals. If due, a pop-up notification would alert the orthodontist or staff, prompting immediate action.
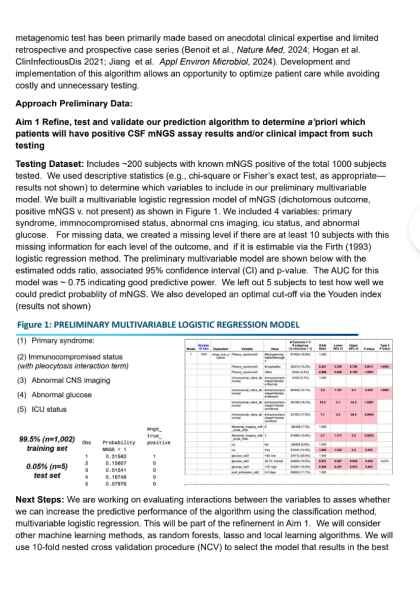
End-users would see these notifications as part of the patient’s digital chart. The recommendations would be explained through a brief summary indicating the last recorded radiograph or cleaning date and the recommended next steps. Users can then schedule the necessary appointments directly from the interface. Additionally, the system may allow customization of reminder frequency based on patient-specific needs. This AI-driven automation would enhance patient care by ensuring timely interventions and reducing reliance on manual tracking.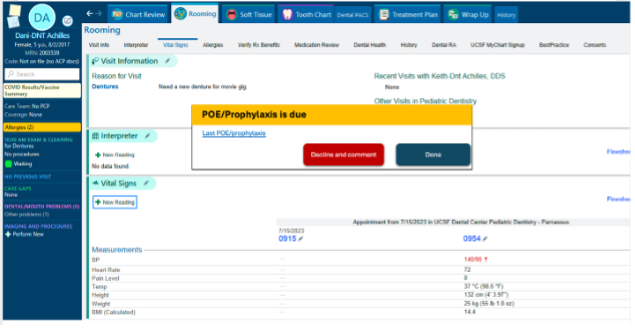
5.What are the risks of AI errors?
6.How will we measure success?
To determine whether the AI system is being effectively used and is achieving its intended goals, we will measure outcomes in two categories: data already being collected in APeX and ideal supplementary measurements.
a. A list of measurements using data that is already being collected in APeX
b. A list of other measurements you might ideally have to evaluate success of the AI
Section 1. The UCSF Health Problem
The UCSF Health Problem
The UCSF Problem:
Lung nodules are a common finding on CT and are often benign but rarely may represent malignancy. To monitor for potential malignancy, follow-up imaging is often recommended. If there is concern for malignancy, adequate follow-up allows earlier diagnosis and treatment, while lack of follow-up may lead to progression and worse prognosis.
The UCSF Health problem
The UCSF Health problem
Patients seek preventive health recommendations from their primary care providers (PCP). Health topics include but are not limited to topics like nutrition, musculoskeletal health, injury prevention, and aging well. These broad topics extend beyond the standard 20-minute annual visit and current APeX-derived healthcare maintenance banner topics.
Tacrolimus is a major immunosuppressive drug in solid organ transplantation.1 Due to its narrow therapeutic index, however, tacrolimus administration requires strict monitoring and adjustment to achieve optimal therapeutic dosages. Excessive dosages may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity while insufficient dosages can lead to acute rejection.2 Consequently, transplant patients require lifelong monitoring of tacrolimus trough concentrations.